arthroscopic surgery
WHAT IS ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY?
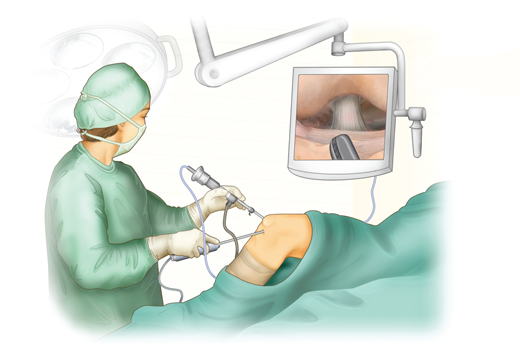
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat joint disorders.. A small, fiber-optic camera implanted into the joint provides your doctor with a close-up picture of the joint, allowing him or her to visualise and correct issues. Arthroscopy is widely used to treat disorders with the shoulder, wrist, elbow, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
Your surgeon may use arthroscopy to examine, assess, and diagnose a joint damage. In certain circumstances, you may require additional treatment or a second procedure to complete the repairs. Damaged cartilage, torn ligaments or tendons, loose bone or cartilage fragments, or an inflammatory joint lining may also be repaired or removed by your surgeon.Arthroscopy is a procedure that is extremely safe and low-risk.
Various types of arthroscopic surgery
Knee:
Because the knee is the most essential joint in the human body, treating it using arthroscopy is the most prevalent procedure. It supports the entire weight of the body and is essential for movement. An average incision on a knee joint is around 4mm long, and irrigation fluid is inserted via this incision for an arthroscope to see the joint area on a video display. Cruciate ligament repair, cruciate ligament reconstruction, meniscus repair, chondroplasty, removal of lost fragments, excision or release of tight structures are among the therapies provided.
Hip:
A hip joint is made up of a ball and socket joint. The ball is a component of the thigh bone, and the socket is a component of the pelvis. Arthroscopy is performed on this joint by making 2-3 tiny incisions about 1 cm long each. The leg is then pulled using a traction device to open up the hip joint. Once the precise location of the damage is determined, surgical instruments are introduced. Hip arthroscopy is used to treat femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia, snapping hip syndromes, synovitis, and hip joint infections. Fragments of bone or cartilage that become loose and move about inside the joint are sometimes treated as well.
Shoulder
A shoulder joint is composed of three bones: the humerus, scapula, and clavicle, as well as four tendons that help hold the joint in place. A shoulder can move more than any other joint in the body. Arthroscopy is performed by 2-3 incisions under general anaesthetic. Arthroscopy of the shoulder joint is recommended for rotator cuff repair, impingement syndrome treatment, and shoulder instability. Inflammation or damage to the joint lining, a damaged biceps tendon, a damaged cartilage ring, spur formation, and recurrent shoulder dislocation are also well treated. Recovery is quicker than with other operations.
Wrist
A wrist’s internal structure is complex, consisting of eight tiny bones and ligaments that link them. Wrist arthroscopy is used to treat recurring strain problems. Chronic wrist pain, wrist fractures, ganglion cysts, ligament fractures, and carpal tunnel release are all treated by arthroscopy.
Spine
The spinal cord is made up of vertebral discs and serves as the command centre for all of our movements. The spinal cord is linked to the brain and aids in the transmission of receptive signals throughout the body via neurons, making it the most sensitive component. The spine is separated into three sections.
(a) Lumbar spine refers to the bottom five discs of your spine, and damage there might cause lower back pain.
(b) The thoracic spine, which is the longest part of your spine, is made up of twelve discs. Ribs are linked here to assist your important internal organs.
(c) The cervical spine is made up of the top seven discs and supports your head and neck.
Even minor spine damage can render you paralysed for the rest of your life. The treatment of the spine is the most difficult. When compared to other traditional surgical approaches, performing arthroscopy on the spine reduces the chances of infection, blood loss, and recovery time. Spinal disc herniation, spinal deformity, tumours, general spine trauma, and degenerative discs can all be treated with arthroscopy.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ):
Temporomandibular joints are the joints that link the jaw to the skull and play a crucial role in chewing food. Arthroscopy for this joint is primarily utilised for non-critical objectives such as releasing adhesions and removing debris and inflammatory mediators from the joint. It is not commonly used.
What conditions treated by arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is widely used to treat the following conditions:
- Inflammation. Synovitis, for example, is a disorder in which the tissues surrounding the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and ankle joint become inflamed.
Acute or chronic injuries, such as:
- Tendon tears in the rotator cuff
- Impingement of the shoulders
- Shoulder dislocations
- Knee meniscus (cartilage) tears
- Chondromalacia
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries cause knee instability.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects the wrist.
- Loose bone and/or cartilage bodies, especially in the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, or wrist
What happens during the procedure?
Your surgeon will create a small incision above the injured joint during the treatment. The doctor will introduce a thin, tiny tube containing a fiber-optic camera. The image of the inside of your joint will be sent to a high-definition monitor for viewing by your surgeon. Your doctor will analyse the damage or injury and, if required, fix it with little instruments. The incision is finally closed and covered.
Recovery
After arthroscopy, you will be able to go home the same day as your operation, and your doctor will provide you with special instructions to aid in your recovery. You may feel some discomfort and tenderness after the treatment, but many patients are able to resume normal activities within a few weeks.
Advantages of minimally invasive surgery
- Incisions that are smaller
- During surgery, there are less problems and bloss loss.
- There is less injury to the surrounding muscle and soft tissues.
- Infection risk is reduced.
- Less post-operative pain and dependency on strong analgesics during recovery
- More rapid recovery and rehabilitation
- Better cosmetic outcomes with less scarring
Call and book your appointment with the best orthopedic surgeon in Mumbai at KK specialty clinic and hospital.
