Purpose of PAP smear test
A Pap smear detects abnormal alterations in the cells of the cervix. Pap smears are used in a variety of medical settings, including:
- Screening: In the absence of symptoms, a Pap smear is most commonly used to screen for cervical cancer. It can detect cervical cancer early on, as well as alterations in cervical cells that may progress to cancer if not treated. When used as a screening test, a Pap smear can be performed alone or in conjunction with a test for human papillomavirus (HPV) strains that can cause cervical cancer.
- A Pap smear can help detect the underlying cause of vaginal symptoms such as irregular vaginal bleeding or discharge.
- A Pap smear can be done as a follow-up test to check for cervical cell abnormalities or other results found during the initial Pap screening.
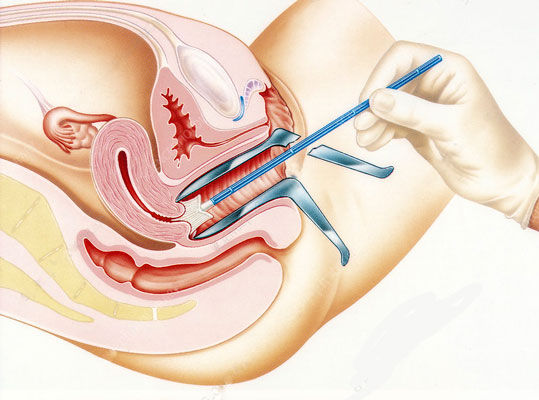
During the procedure:
The Pap test is a painless procedure that takes only a few minutes to complete. The patient is requested to lie down on the back on the examination table with the legs bent. The heels are rested on the stirrups for support. The doctor next inserts or puts a tool called a speculum into the patient’s vagina. The speculum serves to hold the vaginal walls.
The doctor then obtains the samples of the cells of the cervix with the use of a small and soft brush or occasionally with a small scraping instrument known as a spatula. The technique of scraping or collecting cervical cells is absolutely painless.
After the procedure:
The cervical sample is then sent to a lab for further testing to see if cancer cells are present. The collected cervical sample is examined under a microscope for any precancerous or cancerous cells. After the exam, the patient can resume normal activities without difficulty.
What does the test look for?
A Pap smear includes taking a sample of cells from the cervix and inspecting them under a microscope for abnormalities. The findings of a Pap smear show if cervical cells are normal, abnormal, or if the test result is unclear. The type of abnormality detected, as well as the type of cell in which the abnormality was discovered, are used to define abnormal Pap smear results.
When should I get a Pap test?
When a woman with a cervix should get a Pap smear depends on a number of criteria, including age, health, and previous cervical cancer screening. When a patient is pregnant, a healthcare practitioner may additionally prescribe a Pap smear.
Cervical cancer screening may include a Pap smear, an HPV test, or co-testing with both tests performed concurrently. Cervical cancer screening is usually done for all sexually active women every 3 years upto the age of 65 yrs.
Patients should examine the benefits and drawbacks of various screening procedures with their healthcare professional in order to determine which approach is appropriate for their situation.
Schedule your appointment with Dr. Kausha Shah for a PAP smear test and reduce the risk of CA cervix. Dr Kausha Shah is also available at KK medical centre.
Address:ground floor ,gayatri krupa , behind anderpada bus stop, opp. majestic hotel, Dahisar West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400068.